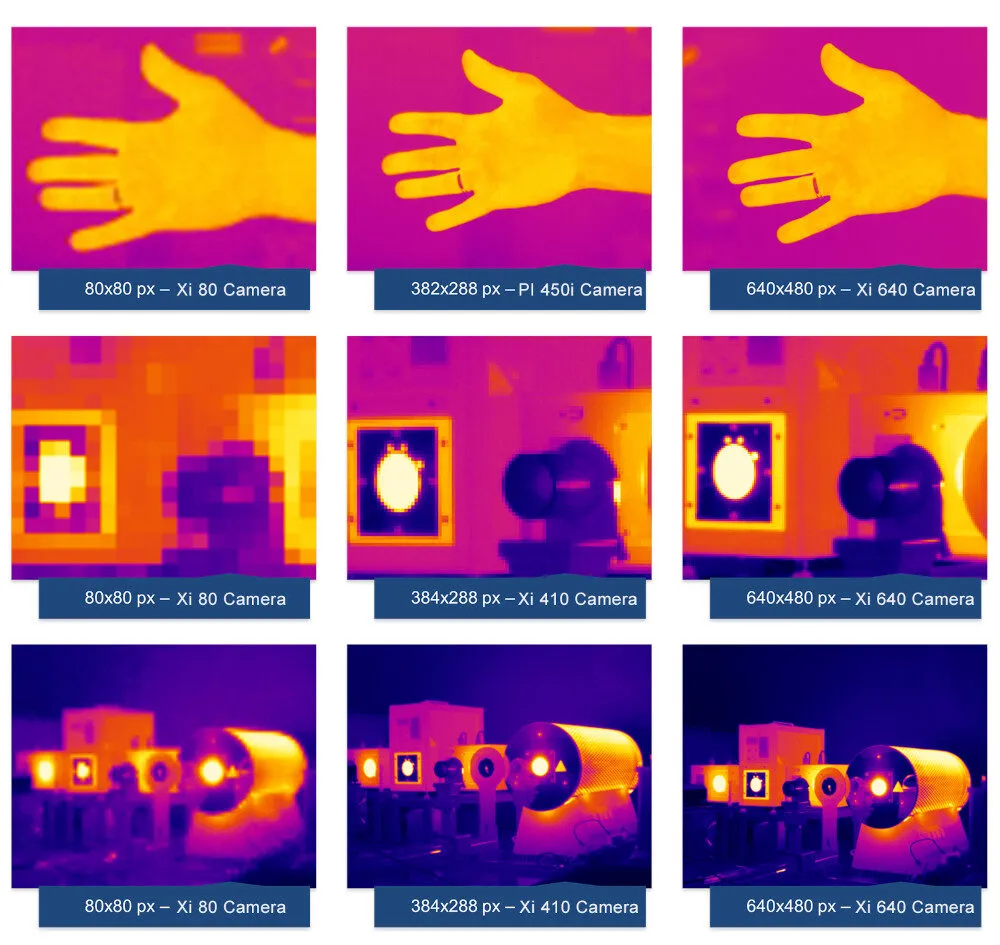
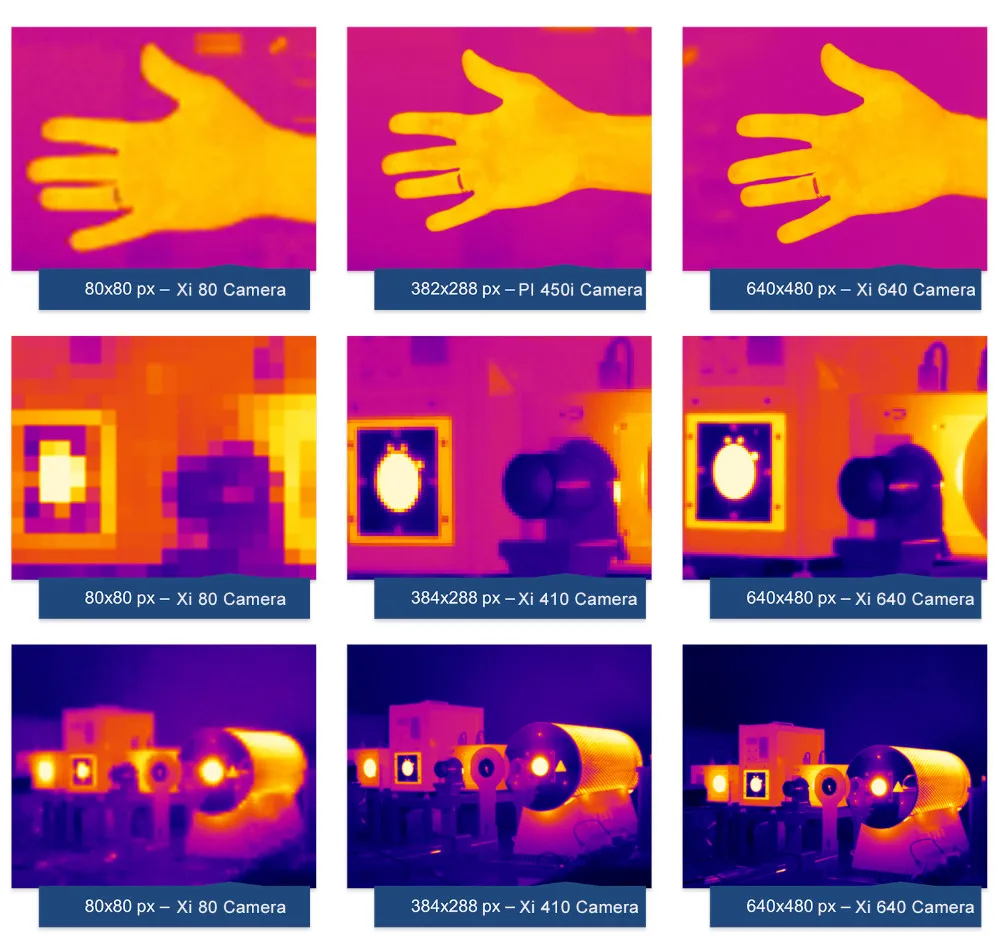
Detector Resolution
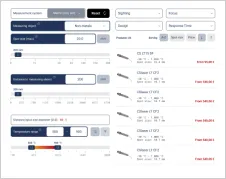
In the context of infrared imaging, detector resolution refers to the number of individual pixels in the infrared detector array and the spatial resolution these pixels provide. It determines the level of detail and clarity in the thermal images produced by the infrared camera. Higher detector resolution means the camera can capture more detailed images, allowing for more precise thermal analysis and identification of smaller features within the observed scene. The resolution of an infrared detector is typically described by the number of pixels arranged in a grid, such as 640 x 480, where 640 represents the number of horizontal pixels and 480 represents the number of vertical pixels. Each pixel in the detector array captures infrared radiation and converts it into an electrical signal, which is then processed to create a thermal image.
Higher detector resolution provides several advantages. It enables the detection of finer details in the thermal image, up to the optical diffraction limits. With more pixels, the infrared camera can capture more temperature data points, leading to more accurate temperature readings and better identification of temperature gradients. Higher resolution can result in clearer and sharper images, making it easier to identify and analyze thermal anomalies.
However, higher detector resolution also demands more from the camera’s processing capabilities and may result in larger data files. It can also be more expensive due to the complexity and precision required in manufacturing high-resolution detectors. Detector resolution directly impacts the detail, accuracy, and quality of thermal images.
Back to LexiconRecommended Products

Talk to us about your IR Temperature Measurement Requirements
Our Infrared Temperature Measurement experts can help you find the right Optris product for your application.