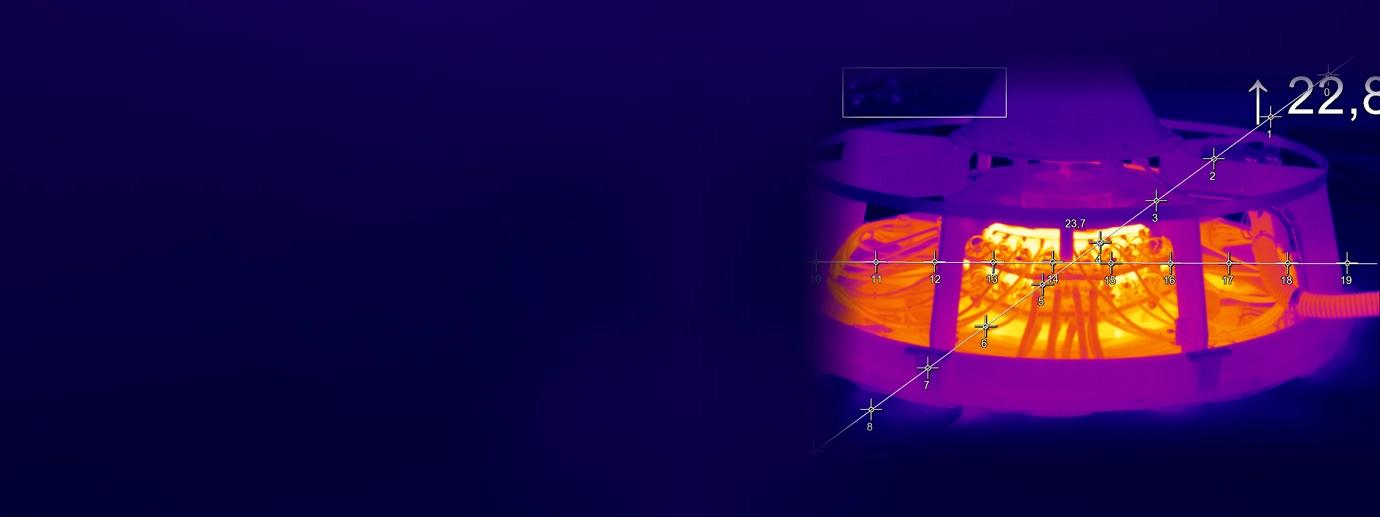
Thermal Monitoring of Brushes in a Dam Turbine
Infrared Temperature Measurement allows Early Fault Detection and Predictive Maintenance
Managing Overheating Risks Carbon Brushes in Hydroelectric Turbines
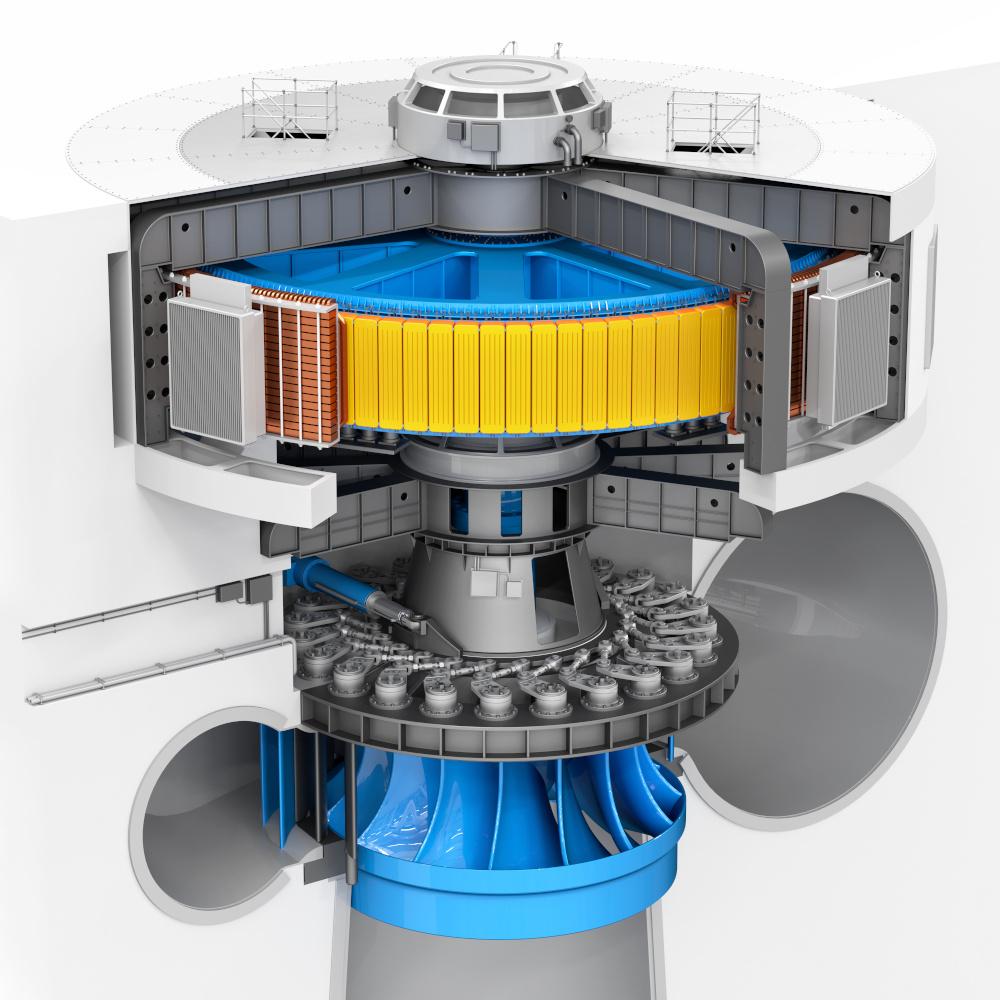
A hydroelectric dam turbine operates by converting the kinetic energy of water into mechanical energy and eventually into electrical energy. Water is directed from a higher-elevation reservoir through pressure pipelines to the turbines. The flowing water strikes the turbine blades, causing them to rotate. This mechanical energy is transferred via a shaft to a generator, which converts the rotational energy into electrical energy.
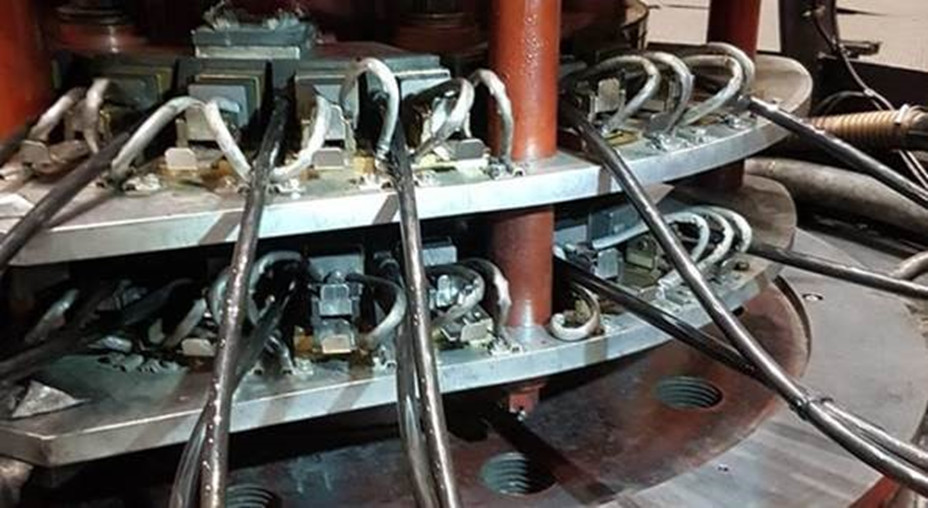
A crucial component in this process is the use of slip rings and carbon brushes, which conduct electricity from the rotating parts of the generator to the stationary parts. Carbon brushes are specially designed carbon-graphite components that are pressed against the rotating commutators or slip rings by spring force. Their primary function is to maintain continuous electrical contact while the generator rotates at high speeds.
However, the use of carbon brushes comes with some technical challenges and potential hazards. A significant danger is overheating. Due to the constant frictional contact, carbon brushes are subject to wear, which generates heat. Inadequate cooling or high operating currents can cause this heat to build up to dangerous levels, raising the temperature of the brushes and surrounding components.
Overheating can lead to several critical consequences. First, it can damage the carbon brushes and slip rings, resulting in increased wear and more frequent maintenance intervals. Second, there is a risk of combustible particles or lubricants igniting due to the high temperatures. This poses a significant fire hazard, especially in the vicinity of generators where large amounts of electrical energy and potentially flammable materials are present.

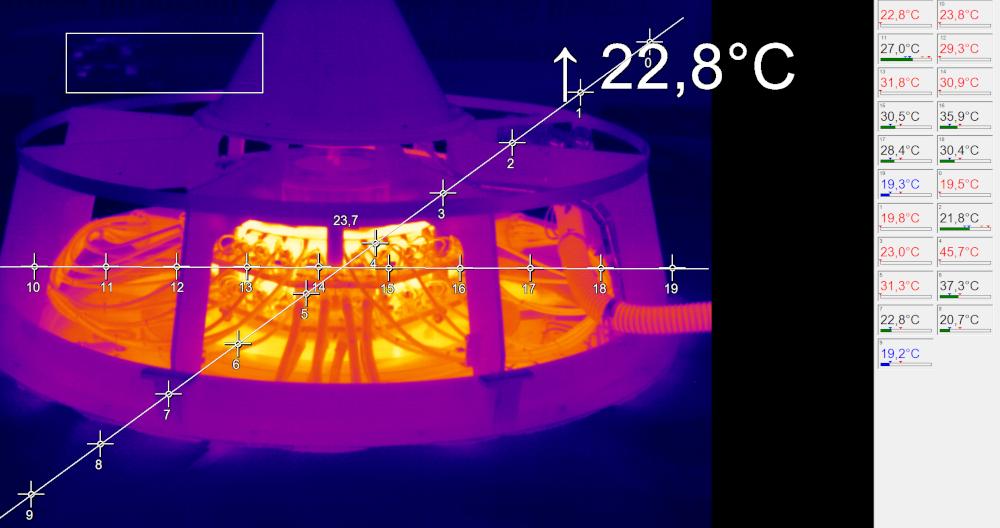
Optimizing Turbine Safety with Infrared Cameras for Thermal Carbon Brush Monitoring
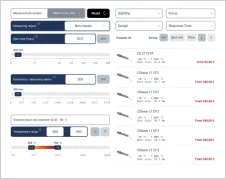
Infrared cameras of the Xi series from Optris are used to monitor the carbon brushes and detect overheating in the early stages. For this purpose, two external boxes are installed on the cover of the turbine, allowing the installation of two Xi cameras (Xi 400 and/or Xi 410) with an angle of 80° and an industrial process interface (PIF). The measuring distance is around 500mm. The recorded thermal data is then continuously transmitted to temperature analysis software, enabling real-time temperature curve analysis. The free PIX Connect analysis software from Optris is ideal for this purpose.
An important aspect is the risk of the environment overheating once the assembly is resealed, leading to ambient temperatures of over 50 °C. Therefore, it is necessary to regulate the internal temperature of the thermal cameras and provide ventilation for the external housings. This prevents the infrared cameras from overheating and ensures they can provide accurate temperature measurements.
As the turbines are not in constant operation and strong vibrations are generated each time they are started, damping is recommended when installing the infrared cameras. This damping minimizes the effects of vibrations on the infrared cameras and protects them from mechanical damage.
Precise infrared monitoring enables reliable monitoring of the carbon brushes and significantly contributes to avoiding overheating risks by issuing timely warnings and thus enabling proactive maintenance measures. This significantly increases the safety and efficiency of the entire system.
Advanced Accessories for Reliable Infrared Monitoring in Tough Conditions
Infrared cameras used in harsh environments must be robust against external influences such as steam, smoke, and high ambient temperatures. These conditions can significantly impact temperature measurements or even render them impossible. Additionally, contamination of the infrared camera’s optics can negatively affect the accuracy of the readings.
To address these challenges, Optris offers a range of accessories that enhance the resilience and efficiency of the Xi series cameras. For instance, the water-cooling housing allows the cameras to operate effectively in hot environments. An air purge attachment and/or a shutter can protect the camera optics from grease and dirt particles, ensuring a clear view of the measurement object. This makes the Optris infrared camera suitable for confined spaces, such as turbine applications.
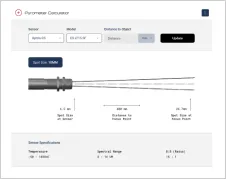
Integration of the infrared camera is also straightforward. With a USB server Gigabit 2.0 and PoE adapter, the camera can be connected to a PC over long distances using PIX Connect. The Xi 400 can be integrated into an industrial PIF and controlled via a PLC, enabling quick and easy integration into existing systems.
The Xi 410 offers the advantage of fully autonomous operation, allowing remote monitoring of turbine systems. With automatic spot search and direct analog or alarm output, it is ideal for condition monitoring and industrial applications.
Recommended Products
Other Condition Monitoring Applications

Talk to us about your IR Temperature Measurement Requirements
There are over 300 different pyrometer variants to choose from in the Optris infrared pyrometer portfolio each optimized for material, spot size, distance from the target, and environmental conditions. Fortunately, there is a trained engineer to phone or chat with to guide you through the process of choosing the perfect infrared sensor for your application.
The same support is available for the extensive IR camera product line.